If you are in any way involved in video recording, you'll have to get to grips with the issue of video formats sooner or later. The most commonly asked question on the topic is: which video format is most suited for my particular purpose? It's a tricky one. Here, we'll shine a light on the topic and explain what's important when it comes to choosing the right kind of video formats. Let's start with the basics.
What actually is a video format?
A video format is a specific type of file format that saves recorded video material and all its associated information. Videos comprise a large number of individual images as well as audio that aligns to these images. Basically any video format is composed of a total of four different values.
- Frame rate (sometimes called frame frequency): This is reproduced in either hertz (Hz) or in frames per second (fps). The higher this value, the more images are used to create the video.
- Color depth: Information on color and brightness values
- Film format: Information on image resolution and on the aspect ratio of the video (e.g. 16:9 or 4:3)
- Audio track: All information regarding the recorded sound
Depending on the resolution, quality and length of the video, the recorded material can be very large and therefore occupy a lot of disk space on the hard drive. To fix this issue, data can be reduced in size using what's known as compression, which results in a file of a smaller size. Depending on compression strength, this file will then require less disk space than the original material. Different video formats work with different types of compression. Of course, this also affects the quality of the recording. Choosing a certain type of video format really depends on where and how the finished video is going to be used.
What video format is best for my project?
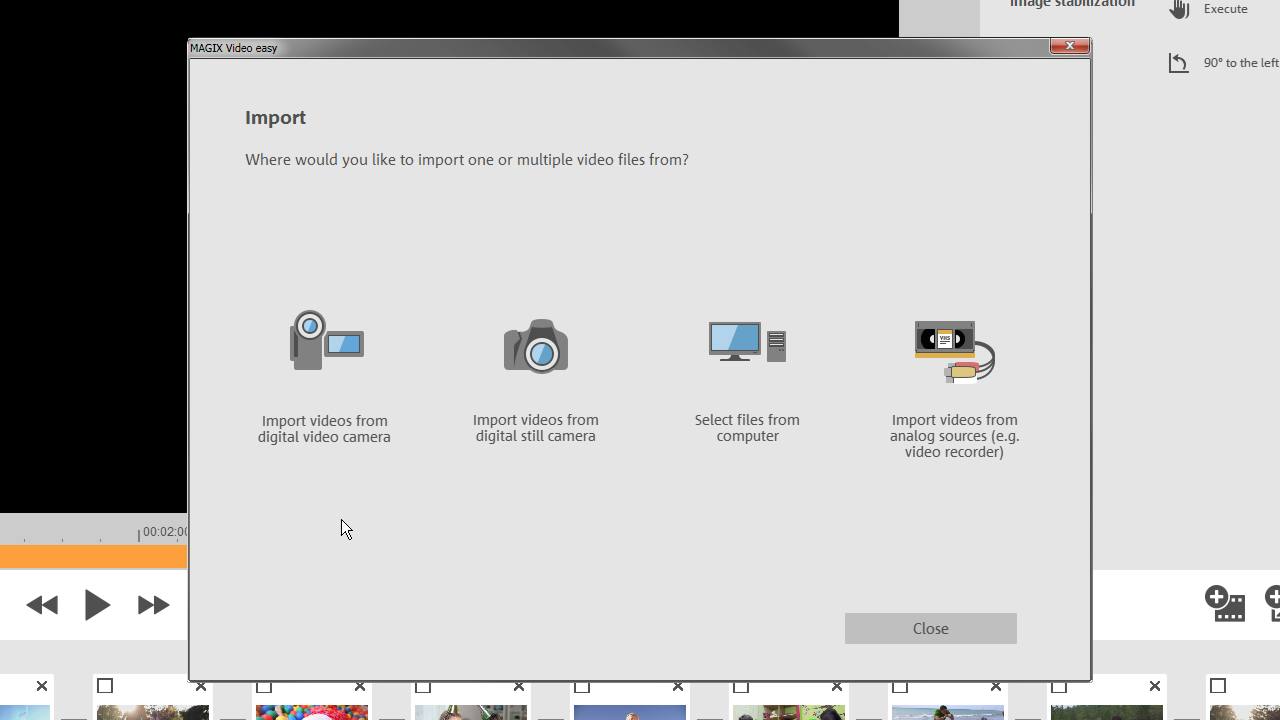
The question of finding the best video format for your needs is not an easy one to answer. But don't worry, with the following information you'll be able to find the right video format in no time at all. If you want to burn your video project to DVD, you'll need a video format for YouTube or Facebook. Or maybe you want to integrate a video you've created into your own website? Not for nothing is use case scenario the decisive factor when it comes to selecting a videos format.
As soon as you record material with a device such as a smartphone, action cam or video camera, the device creates its own, preset video file format. For most devices, you can choose the level of resolution (i.e. quality) of the recorded material beforehand. The lower the resolution, the lower the quality and the smaller the file. Professional video cameras contain other settings in which users can make further adjustments and define a video format for recording.
The most common video formats
Many different formats have been developed over the years, and while some are now used as standard, others have disappeared from the market after a period of time. At first glance, the sheer range of video formats available can seem overwhelming. AVI, MOV, MPEG, FLV etc. – each format has its own strengths and weaknesses. For some formats, the recorded quality of the image and sound takes precedence, while others are for suited for editing. And other formats have a smaller file size, which is a plus because they can be shared on mobile networks without using a high volume of data. Here's a brief overview of various video formats and their essential properties:
AVI
The abbreviation stands for "Audio Video Interleave". The main advantage of this format is that it's one of the most widely used, so it can be used with almost all current multimedia applications. A drawback is that these files are very large in comparison to other video formats and therefore require a lot of disk space.
FLV
The "Flash Video Format" is especially suited for integrating content to websites, since the files are very small. The quality of the video can suffer as a result, however. Also, Adobe Flash Player is required to play back these files – unfortunately, this isn't always supported.
MKV
This "Matroska" format scores points for its wide selection of video and audio tracks as well as text information such as menus, chapters or subtitles and photos, all of which can be contained within the file. The disadvantage of this format is that fewer programs are available for directly editing it, in comparison to other formats.
MOV
Short for "Movie" files, this filename extension for the QuickTime multimedia file format comes from Apple. A plus of this format is that it offers very high quality for relatively lower file sizes. It does require significant computer processing power, however. This format is commonly used in professional and semi-professional domains.
MPEG
Short for "Moving Pictures Experts Group", this format comes in a number of versions. MPEG I and MPEG II are often used for transmitting TV signals, and also for DVDs, while MPEG IV was developed for use on systems with reduced processing power (e.g. smartphones) and lower bandwidth. This enables high image quality for relatively lower file sizes. A heavily compressed MPEG IV file needs to be unzipped by an application before it can be played.
MTS
Video files with this extension use the AVCHD video format (Advanced Video Codec High Definition). This format is often used for recording with consumer HD cameras. While the quality of the recorded video footage is high, the files themselves are very large. Also, this format is compatible with fewer devices and therefore needs to be converted – i.e. changed to another format – before processing.
WMV
Stands for the "Windows Media Video" video format. The benefit of this format is that it requires less storage space to maintain the quality of the original material, meaning that this format is suitable for Internet use. The disadvantage lies with the fact that it is a Windows video format, meaning that it can be difficult or even impossible to play on other systems (e.g. Mac and Linux).
Converting videos:
From one video format to another
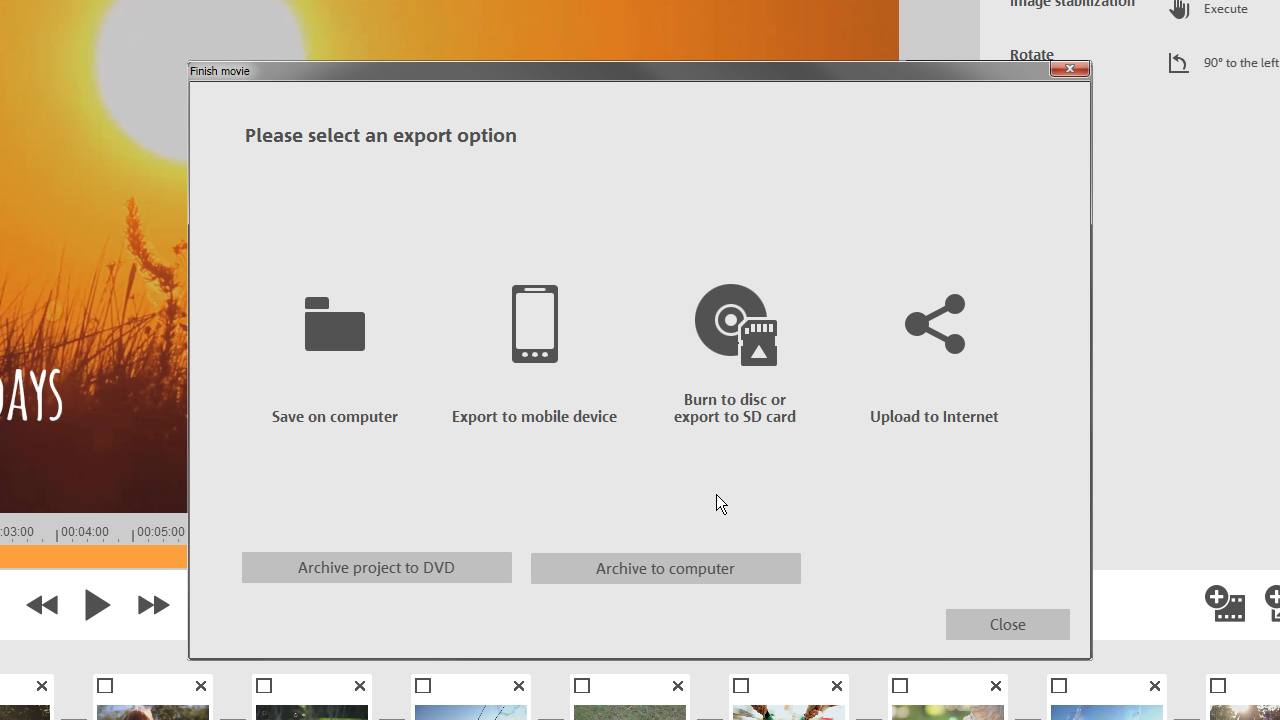
As we've already mentioned, there are a huge number of video formats, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. If you have a certain format to hand, but need a different one, there are a ton of programs that allow you to convert your videos from one format to another. There are a number of ways of doing this, both online and offline. For larger videos with greater disk space, the offline options are best, since if you use an online program, you'll need to upload and then download the video files again. And because video files often exceed gigabyte volume limits, this process can be rather time-consuming.
One thing to note about conversion is that it often can result in a loss in image quality: this depends on the compression and resolution settings. For this reason, before deleting the original video recording after you've converted it into another format, make sure that you are satisfied with the resulting resolution and quality. For more detailed information about converting video formats, see here.
Discover more on what you need to know when it comes to choosing the right kind of video format. No matter what format you choose to shoot with, and no matter what editing you did to the footage, Vegas Pro gives you a full range of format options and templates for export.